Brochure
Acute Low Back Pain
Acute low back pain (LBP) is a common occurrence that most people will suffer from at some point in their lives. There are numerous possible pain producers including muscles, tissue and cartilage damage, the results of which can be present for up to six weeks and initiate mild to severe pain and discomfort. Symptoms are experienced as aching, burning or stabbing pain that may radiate into the buttocks or even thigh/hip area. Ease the pain today by learning more about LBP and reading our recommended treatment.

Emotional Distress
It is quite normal to have emotional reactions to acute back pain. These reactions can include fear, anxiety and worry about what the pain means, how long it will last and how much it will interfere with activities of daily living. Read more about the psychological effects and suggested treatments in this brochure.

Cervical Exercise
Head and neck exercise is just as important as a healthy diet, whether you are having pain or wishing to avoid it, this brochure contains a variety of techniques and head and neck exercises that can help you recover and provide a good defense against future symptoms.
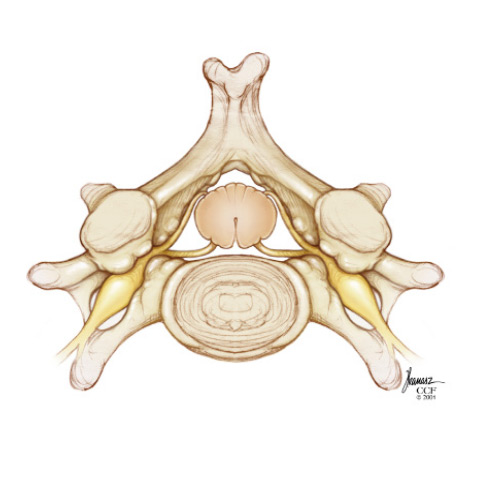
Cervical Stenosis
Cervical Stenosis is a common occurrence in patients over 50 years of age where bones and ligaments thicken and enlarge, pushing into the spinal canal, pinching the spinal cord and nerve roots. Symptoms vary in rate with 50% of patients experiencing pain in the neck or arms, most have symptoms of arm and leg dysfunction, experiencing weakness, stiffness or difficulty in movement. This brochure illustrates the nature of this condition and available treatments.
Chronic Low Back Pain
Low back pain is considered to be chronic if it has been present for longer than three months. Chronic low back pain may originate from an injury, disease or stresses on different structures of the body. The type and intensity of the pain may vary greatly and may be felt as bone pain, nerve pain or muscle pain. A good patient history and a thorough physical examination by a well-trained clinician are the most important aspects of the evaluation. Refer to our brochure for more information on this and how we can help.
EMG
An Electromyogram (EMG) is a non-invasive examination used to assess and evaluate the damage to muscle and nerve function. Patients may experience symptoms including radicular pain (nerve pain radiating from the neck or back), numbness, weakness or tingling in an arm or leg. It is important to find out what is causing your symptoms, reading this brochure is a great place to start.

Exercise
The best low back care includes pain-relieving exercises and proper stretching, followed by moderate strengthening. Taking care of yourself using the illustrated exercises and techniques in this document can help you recover and provide a good defense for preventing future symptoms.
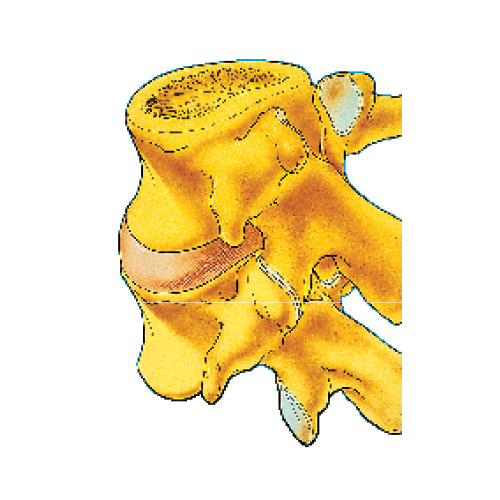
Herniated Cervical Disc
The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called “vertebrae.” The vertebrae surround the spinal cord and protect it from damage. Nerves branch off the spinal cord and travel to the rest of the body, allowing for communication between the brain and the body. The brain can send a message down the spinal cord and out through the nerves to make the muscles move. The nerves also send information such as pain and temperature from the body back to the brain.
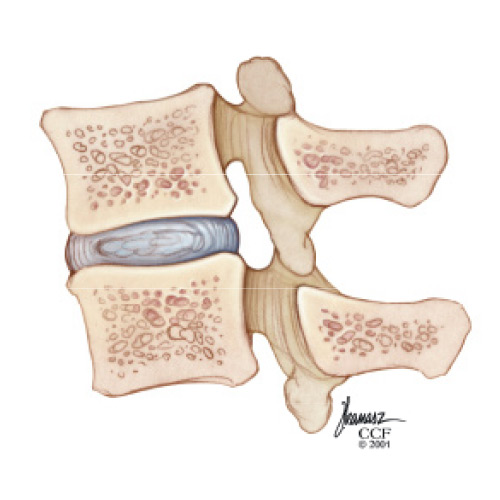
Herniated Lumbar
A herniated lumbar disc can press on the nerves in the spine causing pain, numbness, tingling or weakness of the leg - a condition commonly called “sciatica”. The good news is: 80-90% of patients improve without the need for surgery. Our guide illustrates the treatment and procedures that are used to alleviate the pain and discomfort often experienced with this diagnosis.
MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is typically performed without any special preparation and ordered as part of a medical evaluation. A MRI is relatively risk-free to most people and commonly used to identify the cause of neck, back or radicular pain (pain that radiates from the neck into the arm or lower spine into the leg). Download this brochure for more information on the procedure and how it could help.
NSAIDs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are used to treat inflammation, which often produces or worsens pain by causing stiffness and swelling. Some NSAIDs are available without a doctor’s prescription (“over the counter” or OTC medications). Other NSAIDs are only available with a doctor’s prescription. Our guide illustrates the importance of the correct use, precautions and effects of medication.
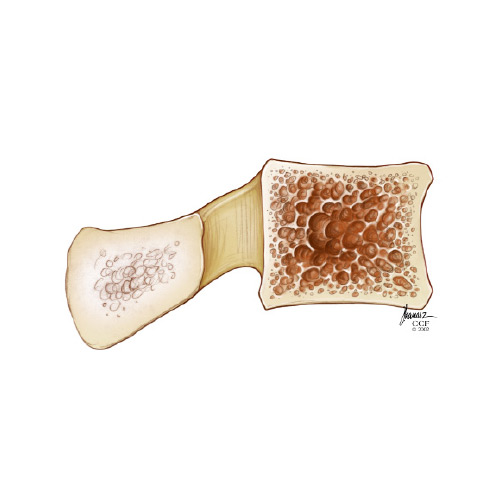
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that affects the bones, causing them to become weak and fragile and more likely to break. Treatment for osteoporosis is based on treating and preventing fractures and using medication to strengthen your bones. It is important that people at risk of osteoporosis take steps to help keep bones healthy and reduce their risk of developing the condition. To learn more about osteoporosis, download our brochure today.
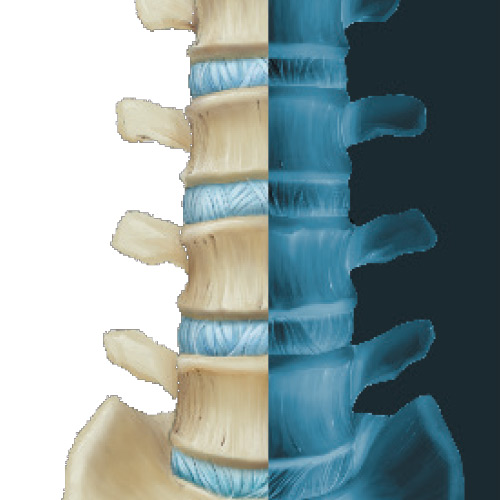
Radiographic
X-ray examinations can be a useful screening tool to assess any bone abnormality of the spine. Most cases of back pain tend to get better without major medical intervention six to eight weeks after the onset of the pain, therefore, X-rays are usually not recommended until after back pain has been present for at least that long. This brochure provides more information on X-rays and how they can help diagnose the problem.
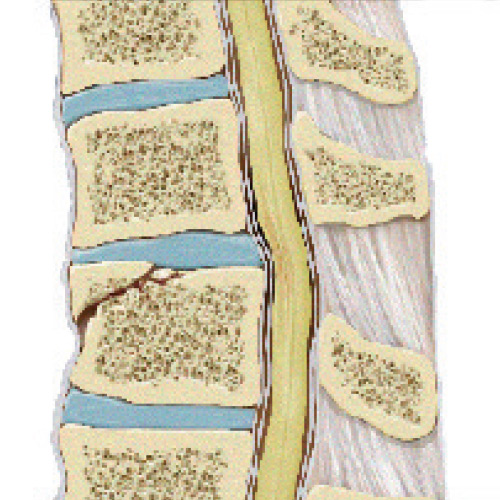
Spinal Cord Injuries
A spinal cord injury is a condition that results from damage or trauma to the nerve tissue of the spine. The diagnosis of these injuries relies upon radiologic studies including X-rays, CAT scans and sometimes magnetic resonance imaging studies (MRI) to visualize the damage. The extent or severity of the spinal cord damage affects prognosis, and treatment will vary accordingly. Download this brochure to learn more about this type of injury.
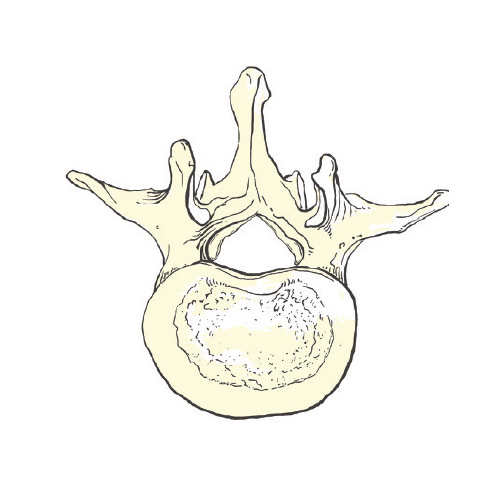
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through the vertebrae and contains the nerves sup- plying sensation and strength to the legs. Between the vertebrae are the intervertebral discs and the spinal facet joints.
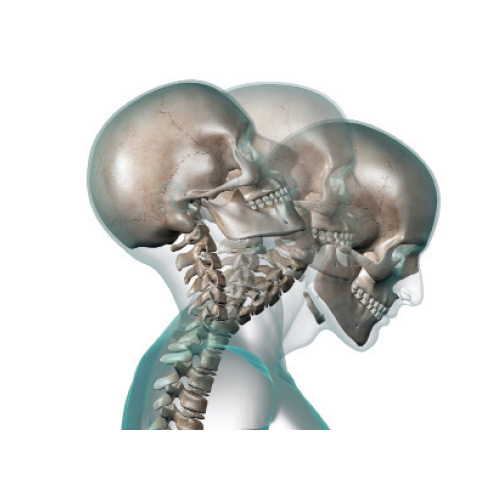
Whiplash
The vigorous movement of the head damages the ligaments and tendons in the neck. A common occurrence as a result of car accidents, patients experience severe discomfort and pain including migraines, neck, shoulder and lower back pain. General recovery takes between 6-8 weeks and nonoperative treatment provides pain reduction and strengthening and conditioning. This brochure provides more information on whiplash and how to recover.
